10 Principles to Develop an Effective Organizational Design
27 Oct


Research by PwC indicates that leading companies are in a near perpetual state of Reorganization. This upsurge in Organizational Design initiatives is owing to the accelerating pace of strategic change caused by disruption of industries, changing competitor landscape, customer behaviors, and distribution channels.
Companies opt to commence efforts to restructure their organization in the hopes of enhancing efficiency, perpetuating growth, and surviving in future. Some shift their Business Models, few alter their focus from products to customer-centric; whereas others adopt new behaviors, systems, or IT architecture. However, merely a quarter of the Organizational Design initiatives succeed in achieving their anticipated objectives.
The reason for this high failure rate is simple. Reorganization is not about changing a company’s organogram. It’s a methodical processes that necessitates transforming / streamlining the decision-making process, mindsets, talent pipeline, reward structures, reporting lines, and the way responsibilities are assigned.
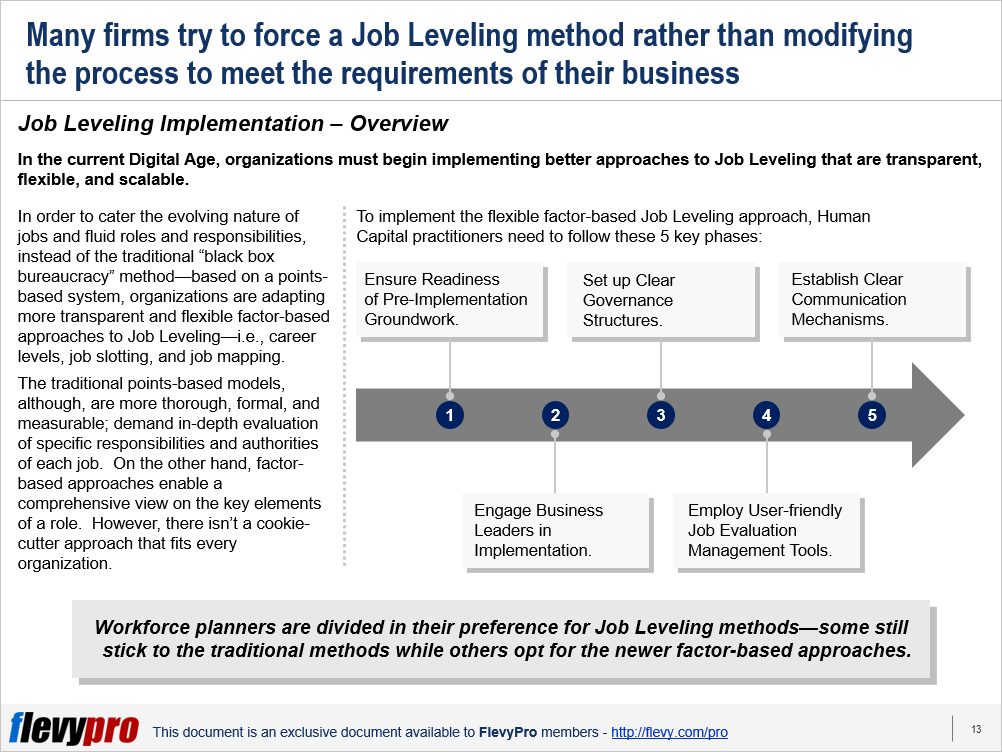
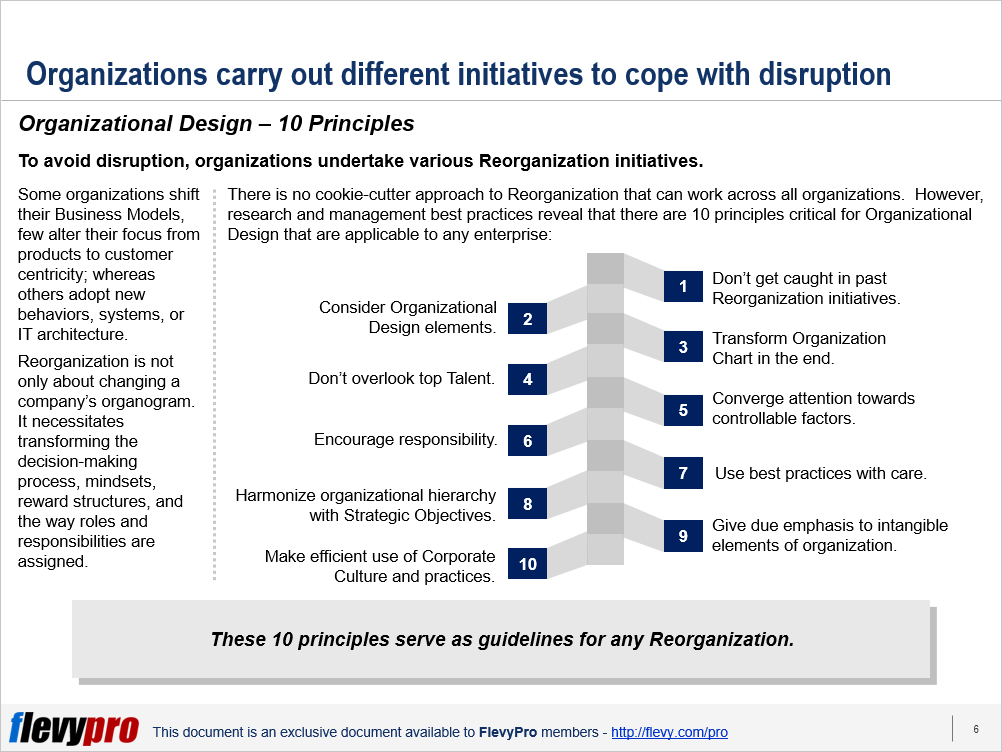
There is no cookie-cutter approach to Reorganization that can work across all organizations. However, research and management best practices reveal 10 principles that are critical for developing an effective Organizational Design, applicable to any enterprise:
- Don’t get caught in past Reorganization initiatives
- Consider Organizational Design elements
- Transform Organization Chart in the end
- Don’t overlook top talent
- Converge attention towards controllable factors
- Encourage responsibility
- Use best practices with care
- Harmonize organizational hierarchy with Strategic Objectives
- Give due emphasis to intangible elements of organization
- Make efficient use of company culture and practices
Let’s dive deeper into these guiding principles.
1. Don’t Get Caught in Past Reorganization Initiatives
Leaders at most organizations tend to keep discussing and focusing on the old reorganization initiatives. This takes away much of their time and energy which should rather be spent on making the current Organizational Design a success.
Organization Design should be created on the basis of an enterprise’s sense of purpose, strategy, core competencies, products, competitive advantage, and experience offered to customers and employees. Senior leaders need to be able to see the broader perspective, set clear organizational objectives, and steer the workforce to achieve their personal as well as organizational objectives.
2. Consider Organizational Design Elements
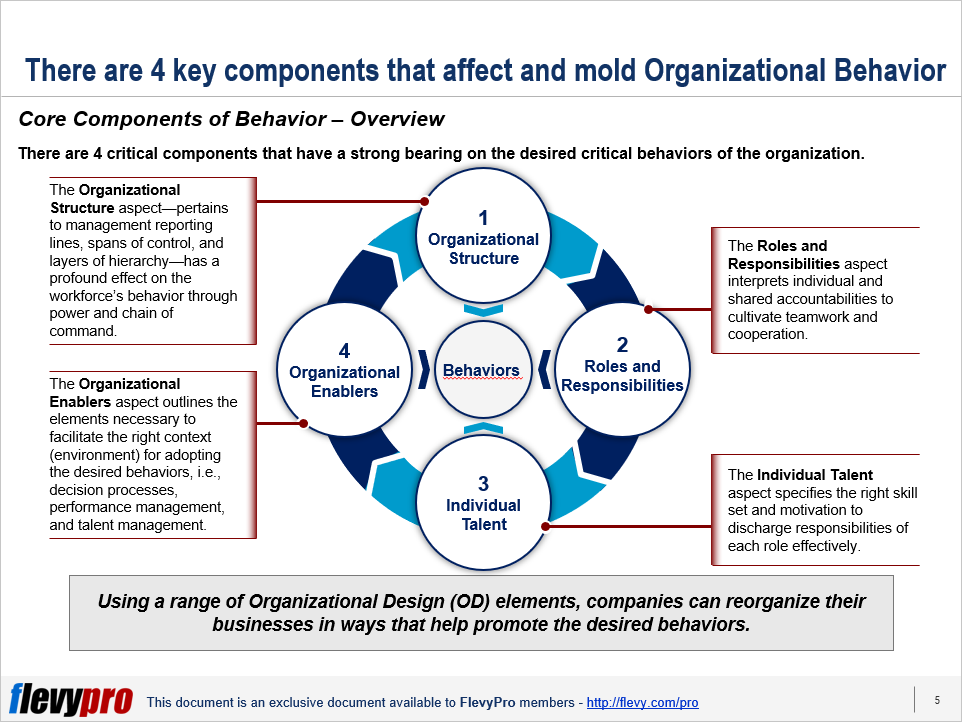
Reorganization is a complex undertaking, but a structured approach to Organizational Design assists in identifying and prioritizing key priorities. Organizational Design has 8 fundamental elements that are important for all organizations, Business Models, sectors, or regions. These elements can be categorized into 4 pairs. Each of these 4 pairs constitute a formal (tangible) and an informal (intangible) element:
- Decisions team up with Norms (the way people act).
- Motivators (the way people are influenced to work) pair with Commitments (what affects people’s thoughts about work).
- Information (the way data is processed) pairs with Mindsets (how people process knowledge and meaning).
- Structure (reporting lines) pairs off with Networks (how people collaborate).
Leaders should select fewer, prioritized Organizational Design elements to work on that have the most impact on their organizations.
3. Transform Organization Chart in the End
Most leaders consider Organization Structure to be the most critical element to Business Transformation. In reality, there are other key organizational elements that need to be tackled first to improve effectiveness. Revisiting the organogram does not have much effect on the way business is done—or to improve it. Structure depicts reporting lines and changing it can reduce costs temporary. Changing structure alone—without transforming other organizational elements—allows the redundant reporting lines to reappear and put the organization back to its earlier state of affairs. Instead of changing the organogram, core organizational issues should be prioritized and confronted first. Structure will adjust accordingly once the issues resolve.
4. Don’t Overlook Top Talent
Top talent often go unnoticed when it comes to Reorganization. The skills and traits of the senior leadership has a profound impact on Organizational Design. Mapping of technical capabilities and leadership abilities of top leadership is an important step to Reorganization.
Interested in learning more about the guiding principles critical for Organizational Design?” “You can download an editable PowerPoint on 10 Principles of Organizational Design here on the Flevy documents marketplace.
Do You Find Value in This Framework?
You can download in-depth presentations on this and hundreds of similar business frameworks from the FlevyPro Library. FlevyPro is trusted and utilized by 1000s of management consultants and corporate executives. Here’s what some have to say:
“My FlevyPro subscription provides me with the most popular frameworks and decks in demand in today’s market. They not only augment my existing consulting and coaching offerings and delivery, but also keep me abreast of the latest trends, inspire new products and service offerings for my practice, and educate me in a fraction of the time and money of other solutions. I strongly recommend FlevyPro to any consultant serious about success.”
– Bill Branson, Founder at Strategic Business Architects
“As a niche strategic consulting firm, Flevy and FlevyPro frameworks and documents are an on-going reference to help us structure our findings and recommendations to our clients as well as improve their clarity, strength, and visual power. For us, it is an invaluable resource to increase our impact and value.”
– David Coloma, Consulting Area Manager at Cynertia Consulting
“FlevyPro has been a brilliant resource for me, as an independent growth consultant, to access a vast knowledge bank of presentations to support my work with clients. In terms of RoI, the value I received from the very first presentation I downloaded paid for my subscription many times over! The quality of the decks available allows me to punch way above my weight – it’s like having the resources of a Big 4 consultancy at your fingertips at a microscopic fraction of the overhead.”
– Roderick Cameron, Founding Partner at SGFE Ltd