Corporate Functional Strategy
26 Feb


The role of corporate functions, traditionally, has been to conduct the various service-oriented specialized tasks necessary to run the business. Corporate functions are of strategic significance in achieving organizational objectives yet their role at most enterprises is kind of contractual at best. These units assist in routine operations, facilitate other business units, and manage conflicts and relevant pressing matters. For instance, the Human Resources (HR) function is typically responsible for staffing people, administering their benefits, managing performance appraisals, and career advancement procedures.
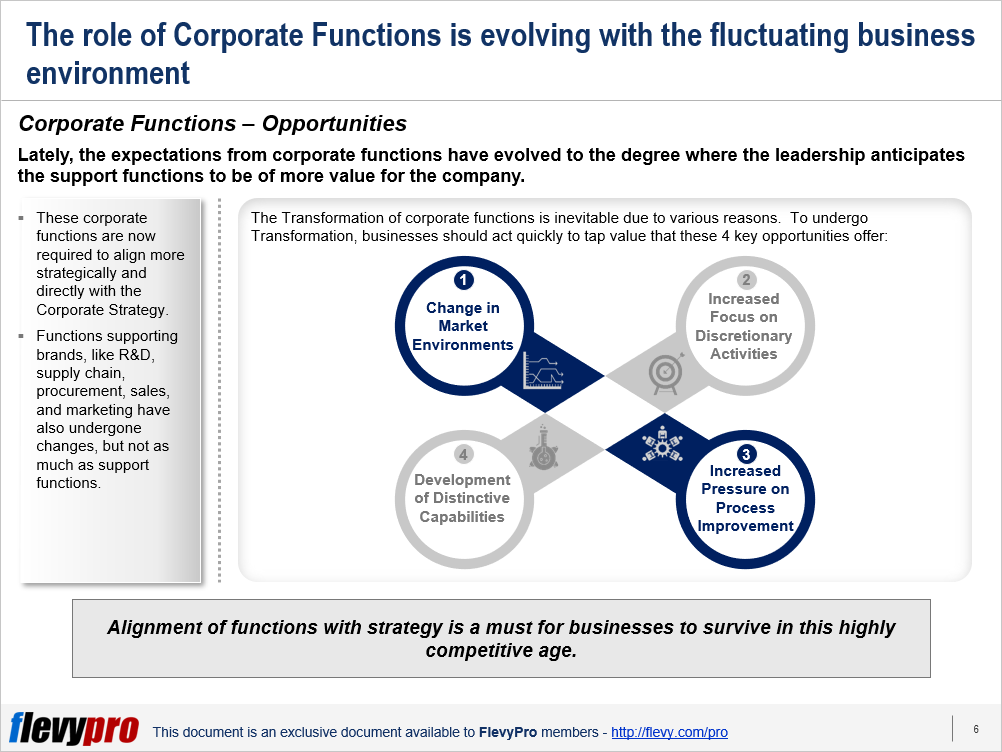
Constant pressure on businesses to compete in this age of disruption has forced them to rethink the role of their Corporate Functions. Lately, the expectations from corporate functions have evolved to the degree where the Leadership anticipates the support functions to be of more value for the company. These corporate functions are now required to align more strategically and directly with the Corporate Functional Strategy.
To undergo Transformation, businesses should act quickly to tap value offered by these 4 key opportunities:
- Change in Market Environments
- Increased Focus on Discretionary Activities
- Increased Pressure on Process Improvement
- Development of Distinctive Capabilities
Let’s delve deeper into these key opportunities.
Change in Market Environments
Markets are becoming more and more volatile, uncertain, and rife with innovative rivals. In addition, the constantly shifting customer demands are forcing organizations to put more pressure on strategic as well as support functions. This demands from these functions to develop expertise in order to deliver on more complex tasks than in the past. For instance, IT needs to be able to now design applications capable of unearthing vast data lakes to reveal valuable insights in real-time.
Increased Focus on Discretionary Activities
Traditional corporate functions were more occupied with routine operational activities—resolving financial errors, emailing, overseeing employee compensation, and managing IT assets. However, now, thanks to Process Optimization and Outsourcing, Corporate Functions have become efficient to the point that they have slashed the requirement for resources to deal with routine activities significantly. This has freed immense resources, leaders’ time and effort to be spent on discretionary strategic initiatives that have the potential to bring more value for the organization.
Increased Pressure on Process Improvement
Changing market dynamics and intensifying rivalry has strained the organizations to ensure seamless implementation of strategic initiatives, boost effectiveness, and bring on Operational Excellence. This competitive landscape has forced the functional leadership to reduce expenditures, find new avenues of operational improvement, and enhance value.
Development of Distinctive Capabilities
The changing market dynamics have made the companies realize the significance of creating unique capabilities—differential edge acquired due to the ability to do things remarkably and inimitably. Organizations are now more focused on empowering their global corporate employees. The Corporate Functions have now become more and more important for the organization’s Corporate Strategy. Rather than just assessing fulfillment of requests from the team members, rewards and recognition of functional leaders is now being tied more with their efficiency, judgment, ability to create key differentiators for the organization, and finding efficient ways of doing business.
Organizations are now more focused on empowering their global corporate employees. Rather than just assessing fulfillment of requests from the team members, rewards and recognition of functional leaders is now being tied more with their efficiency, judgment, ability to create key differentiators for the organization, and finding efficient ways of doing business.
Interested in learning more about Corporate Functional Strategy? You can download an editable PowerPoint on Functional Strategy here on the Flevy documents marketplace.
Do You Find Value in This Framework?
You can download in-depth presentations on this and hundreds of similar business frameworks from the FlevyPro Library. FlevyPro is trusted and utilized by 1000s of management consultants and corporate executives. Here’s what some have to say:
“My FlevyPro subscription provides me with the most popular frameworks and decks in demand in today’s market. They not only augment my existing consulting and coaching offerings and delivery, but also keep me abreast of the latest trends, inspire new products and service offerings for my practice, and educate me in a fraction of the time and money of other solutions. I strongly recommend FlevyPro to any consultant serious about success.”
– Bill Branson, Founder at Strategic Business Architects
“As a niche strategic consulting firm, Flevy and FlevyPro frameworks and documents are an on-going reference to help us structure our findings and recommendations to our clients as well as improve their clarity, strength, and visual power. For us, it is an invaluable resource to increase our impact and value.”
– David Coloma, Consulting Area Manager at Cynertia Consulting
“FlevyPro has been a brilliant resource for me, as an independent growth consultant, to access a vast knowledge bank of presentations to support my work with clients. In terms of RoI, the value I received from the very first presentation I downloaded paid for my subscription many times over! The quality of the decks available allows me to punch way above my weight – it’s like having the resources of a Big 4 consultancy at your fingertips at a microscopic fraction of the overhead.”
– Roderick Cameron, Founding Partner at SGFE Ltd